The ocean covers more than 70% of our planet, yet beneath its shimmering surface lies an escalating environmental crisis. Sea pollution facts reveal alarming truths about how human activities are endangering marine ecosystems and, ultimately, our own survival. From toxic plastic waste to chemical runoff, the sea is absorbing the consequences of industrialization, negligence, and overconsumption. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the facts about sea pollution, explore its causes, types, and effects, and uncover what we can do to restore ocean health. Understanding these realities is not just an environmental duty it’s essential for the future of both marine life and humankind.

What Is Sea Pollution?
At its core, sea pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances into oceans and seas, disrupting marine ecosystems and endangering biodiversity. These contaminants come from land-based sources like factories, agriculture, sewage, and plastic waste. According to the United Nations, nearly 80% of marine pollution originates from land-based human activities.
Historically, sea pollution facts were overlooked until the mid-20th century when industrialization began dumping massive amounts of waste into water bodies. Oil spills, plastic debris, and chemical discharges have since become constant threats. The awareness of marine pollution facts grew only after the discovery of massive “garbage patches” floating in oceans grim symbols of human neglect.
The Major Types of Sea Pollution
Plastic Pollution in Oceans
One of the most disturbing sea pollution facts is that about 8 million tons of plastic enter the ocean every year. From disposable bottles to fishing nets, plastics break down into microplastics that are ingested by fish, seabirds, and even humans. These pollutants poison marine species and disrupt the entire food chain.
Quick Facts:
- Over 100,000 marine animals die each year from plastic entanglement.
- Microplastics are found in 94% of tap water samples globally.
- Plastic pollution costs up to $13 billion annually in economic damages to marine ecosystems.
Oil Spills and Chemical Runoff
Another shocking aspect of sea pollution facts is the role of oil spills and chemical runoff. When oil leaks into the ocean, it coats marine life, blocking oxygen exchange and suffocating coral reefs. Industrial and agricultural chemicals such as pesticides and fertilizers flow into seas through rivers, creating “dead zones” where no aquatic life can survive.
Examples: The Deepwater Horizon oil spill (2010) released over 200 million gallons of crude oil into the Gulf of Mexico, devastating marine habitats for years.
The Hidden Impact on Marine Life and Human Health
Harm to Marine Ecosystems
Sea pollution facts highlight that marine ecosystems are being destroyed faster than they can recover. Coral bleaching, loss of biodiversity, and toxic contamination are rampant. Heavy metals like mercury and lead accumulate in fish, which then enter human diets, causing severe health risks.
Effects include:
- Genetic mutations in marine species
- Destruction of coral reefs, the “rainforests of the sea”
- Disruption of food chains and oxygen levels in water
Threats to Human Health
Few people realize that sea pollution facts poses a direct danger to humans. When we consume seafood contaminated with microplastics or mercury, these toxins accumulate in our bodies. Long-term exposure can lead to neurological damage, cancer, and hormonal imbalances.
Sea pollution facts also show that polluted beaches and coastal waters increase risks of skin infections and gastrointestinal diseases.
Real-World Examples of Sea Pollution
- The Great Pacific Garbage Patch – A floating island of waste twice the size of Texas, representing one of the most devastating sea pollution facts in existence.
- Minamata Bay, Japan – Industrial mercury discharge in the 1950s caused severe neurological disorders in thousands, now known as “Minamata Disease.”
- Baltic Sea Dead Zones – Nutrient pollution has led to large oxygen-deprived areas, threatening fish stocks and livelihoods.
These examples remind us that sea pollution facts is a global issue with lasting consequences.
Why Sea Pollution Matters
The importance of sea pollution facts lies in understanding the connection between ocean health and human survival. Oceans regulate climate, produce oxygen, and provide food and jobs for billions. When the seas suffer, humanity suffers too.
Key challenges include:
- Lack of waste management in developing nations
- Weak enforcement of international pollution laws
- Rising global consumption of plastic products
- Climate change intensifying ocean acidification
Overcoming these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable practices, and public awareness.
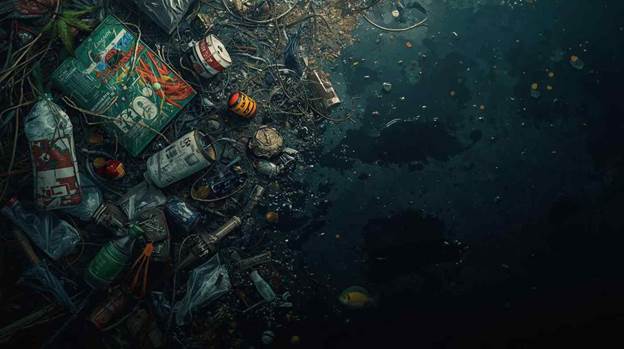
Solutions and Prevention Strategies for Sea Pollution
Global Efforts and Environmental Policies
Organizations like the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and Ocean Conservancy are spearheading campaigns to reduce marine waste. The Clean Seas Campaign aims to eliminate single-use plastics by 2030.
Effective measures:
- Implement stricter waste disposal laws
- Support eco-friendly packaging alternatives
- Strengthen marine protection zones
- Promote ocean cleanup initiatives
What Individuals Can Do
You don’t have to be a scientist to make a difference. Here are practical ways to combat sea pollution facts :
- Reduce plastic use and recycle properly
- Participate in local beach cleanups
- Support sustainable seafood choices
- Educate others about sea pollution facts
Even small actions, when multiplied globally, can help restore ocean balance.
Conclusion
The truth behind sea pollution facts is both alarming and motivating. From plastics and oil spills to chemical waste, our oceans face unprecedented threats that demand urgent attention. Understanding these facts about sea pollution empowers individuals and communities to act responsibly. By supporting sustainable practices and spreading awareness, we can protect marine life and secure a healthier future for all. Let’s keep our oceans clean because when the seas thrive, the planet thrives too.
